News
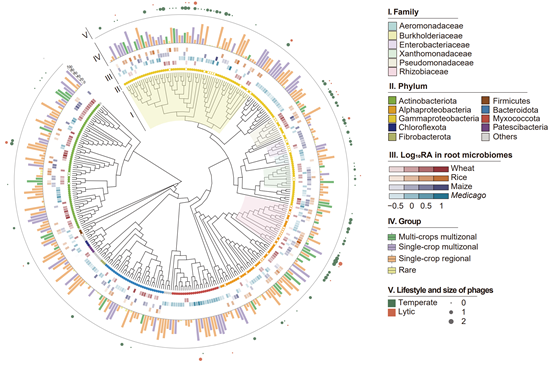
Crop root bacterial and viral genomes reveal unexplored species and microbiome patterns
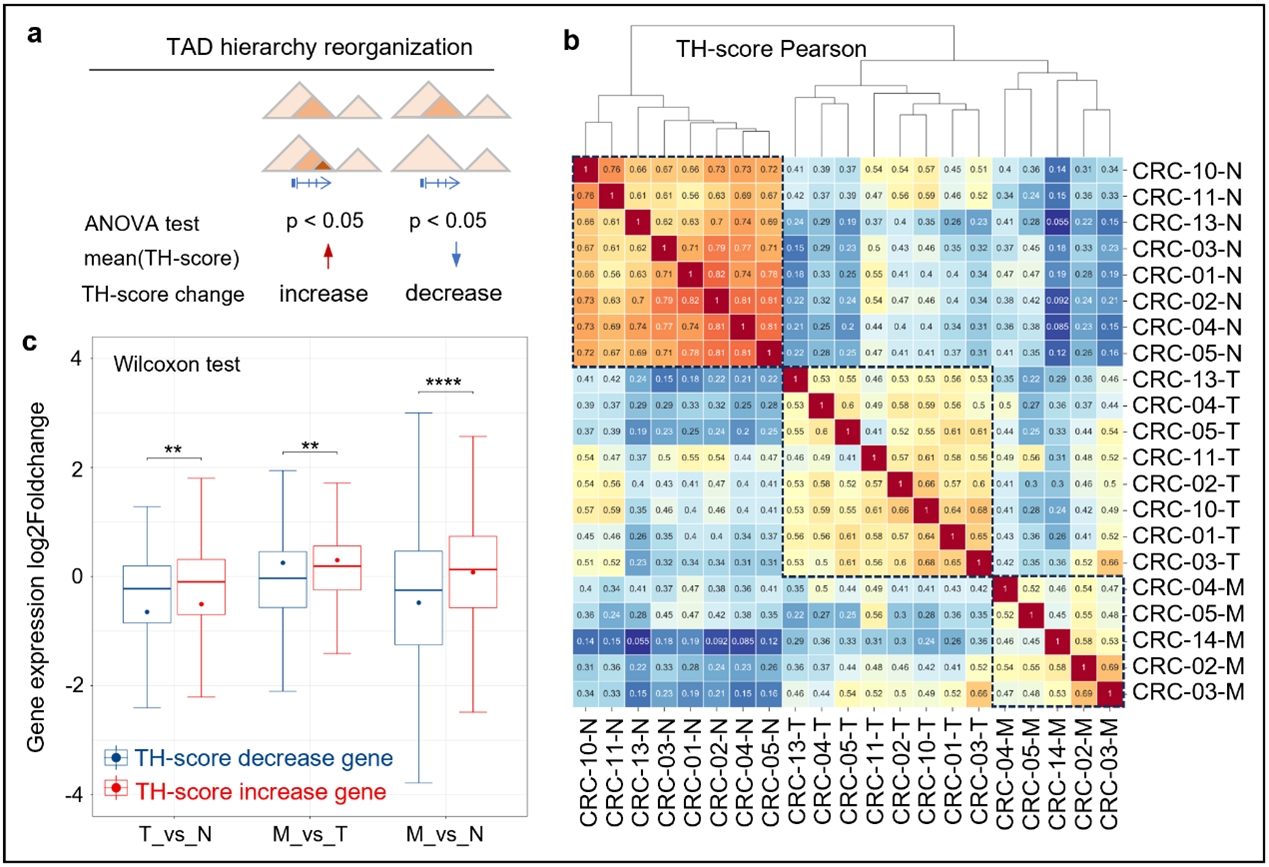
3D genome landscape of primary and metastatic colorectal carcinoma reveals the regulatory mechanism of tumorigenic and metastatic gene expression

CTDP1 and RPB7 stabilize Pol II and permit reinitiation
The mechanisms governing the termination and subsequent reinitiation of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) remain poorly understood. Here we find that depletion of RPB7 leads to the destabilization of Pol II’s largest subunit, RPB1.
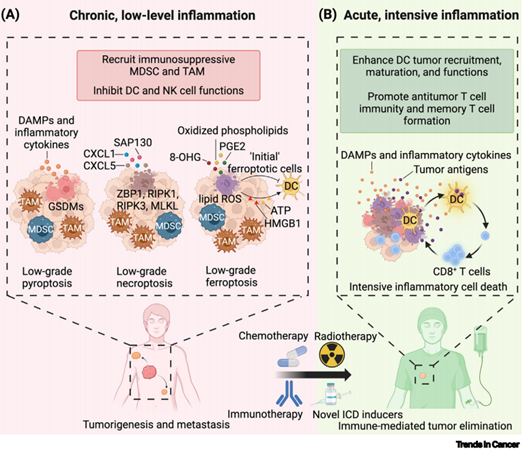
Dying to survive: harnessing inflammatory cell death for better immunotherapy
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment paradigms, but its effectiveness depends largely on the immunogenicity of the tumor. Unfortunately, the high resemblance of cancer to normal tissues makes most tumors immunologically ‘cold’, with a poor response to immunotherapy.
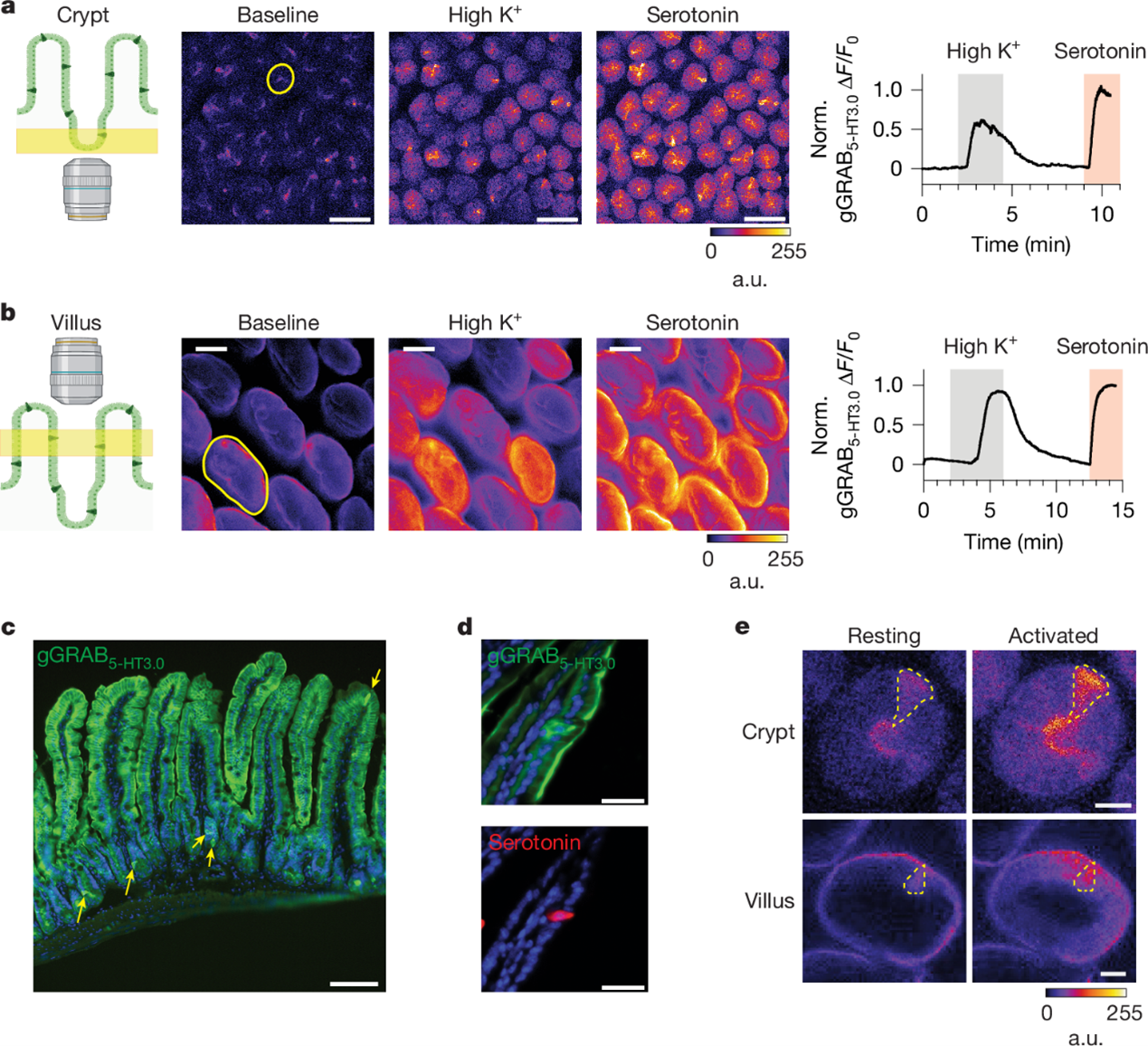
Topological segregation of stress sensors along the gut crypt–villus axis
The crypt–villus structure of the small intestine serves as an essential protective barrier. The integrity of this barrier is monitored by the complex sensory system of the gut, in which serotonergic enterochromaffin (EC) cells play an important part.




